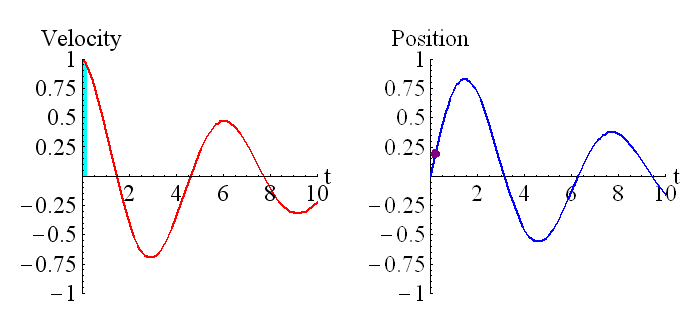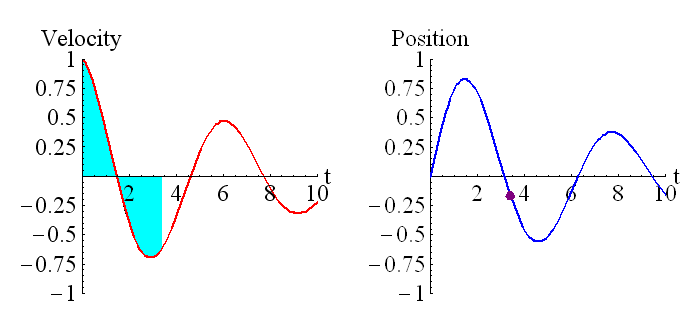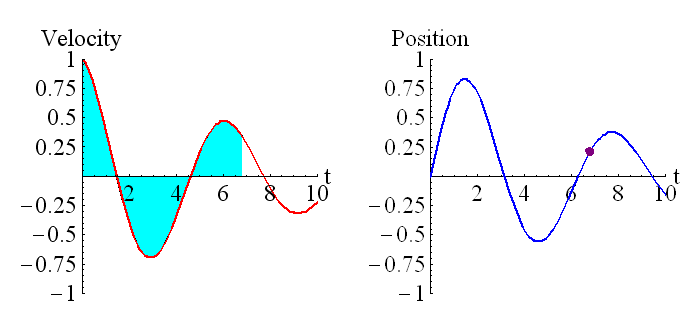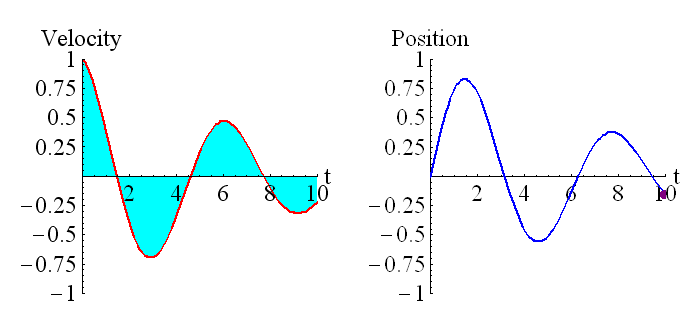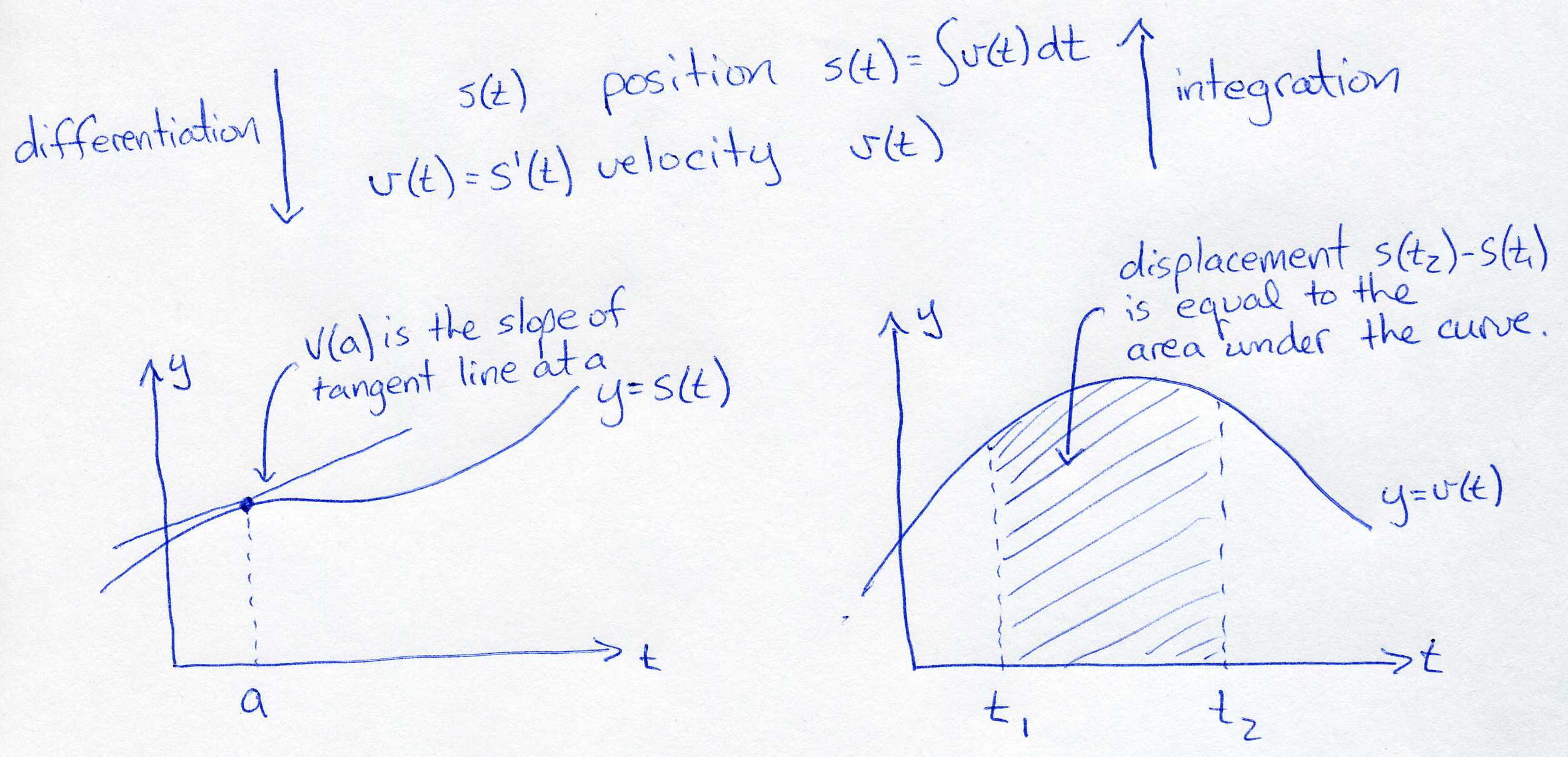
This picture shows the relationship between position and velocity, and derivatives and integrals.

Let us look at some animations of this, to get a better feel for it. In what follows, we will set t1=0.
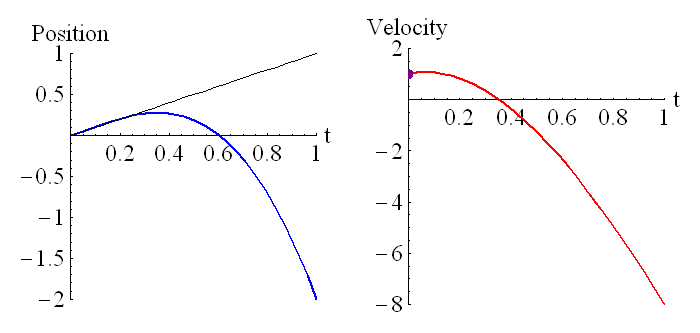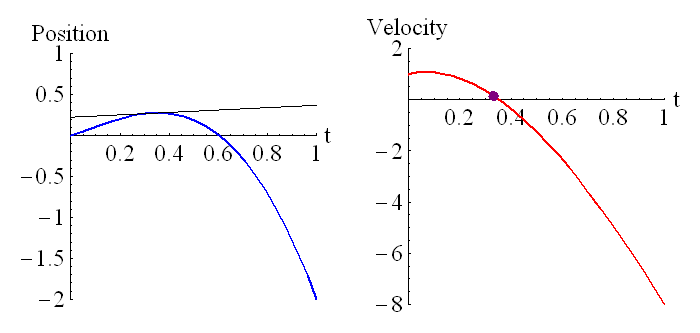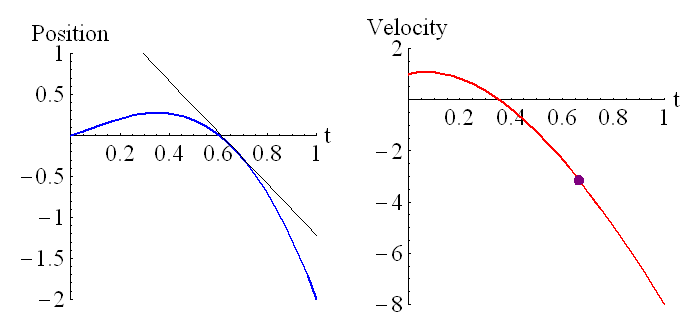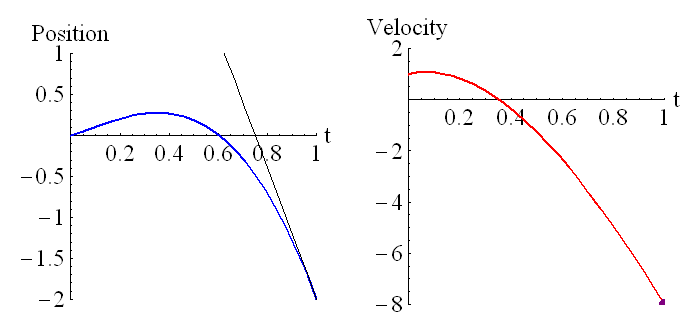
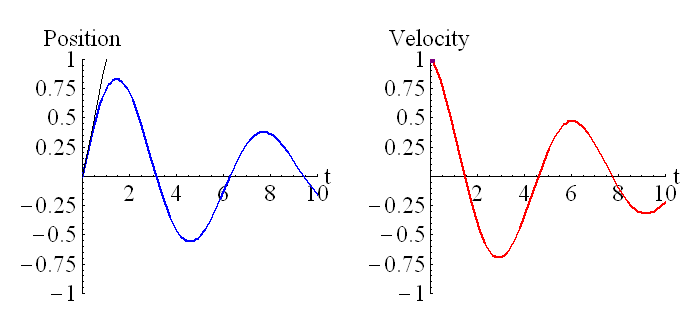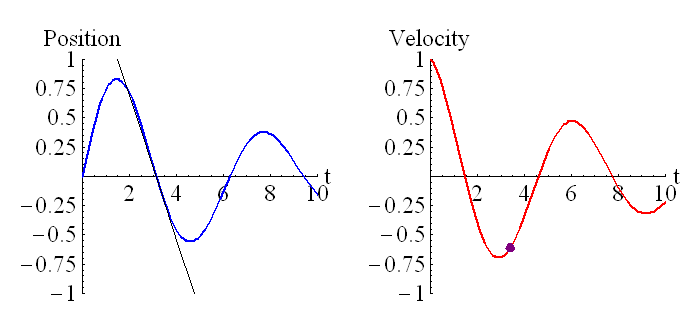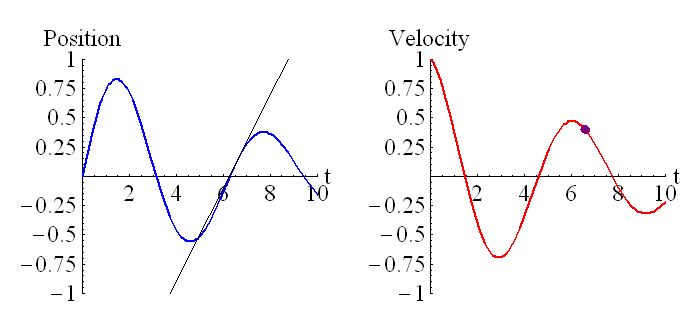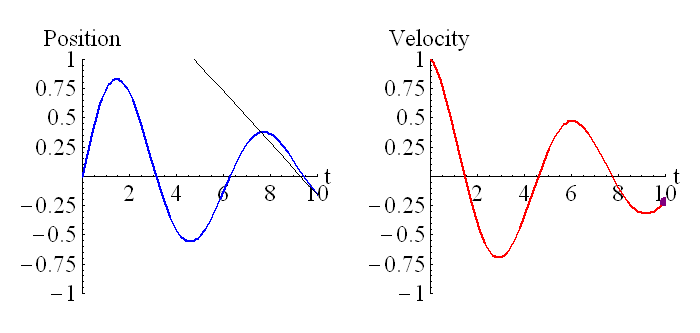
The above animation shows how the velocity is related to the derivative of the position. The purple dot on the graph on the right represents the slope of the tangent line of the graph on the left.
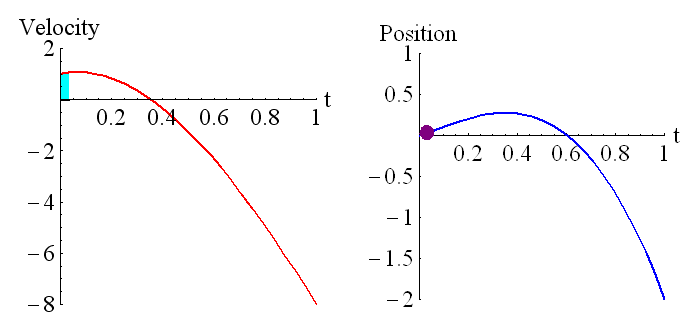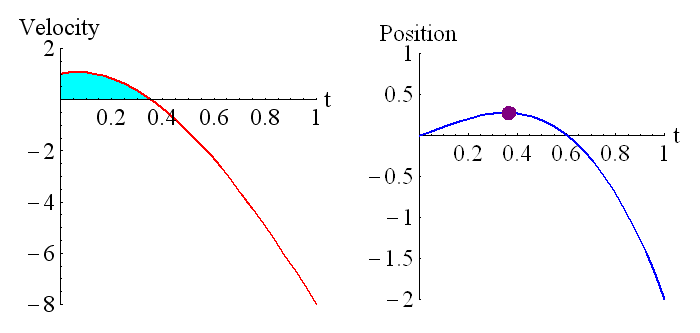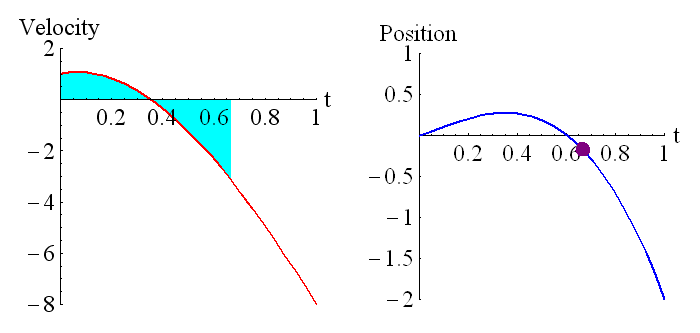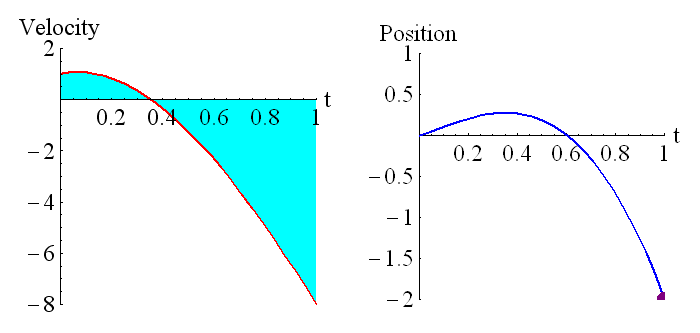
The above animation shows how the position is related to the integral of the velocity. The purple dot on the graph on the right represents the shaded region of the graph on the left. Remember that regions under the t axis are considered negative, so this is the net area under the curve. We can see that around t=0.6 the particle has returned to its starting position (position is zero, which is where it started), and the particle is moving in the opposite direction to when it started moving (velocity has changed sign).
Here is another example, for a particle that is oscillating back and forth, with the oscillations becoming smaller. Notice that when the velocity is zero, the particle starts moving in the other direction.